
Single Slit Diffraction is that which produces refraction, interference, diffraction, reflection, etc when light travels in the air.It is defined as the source of light and the screen in which the pattern of diffraction is obtained effectively at the limited or finite distance from the diffracting system. Fresnel Diffraction occurs due to size of the obstruction.Fraunhofer Diffraction is defined as the source of light and the screen in which the pattern of diffraction is obtained effectively at the limitless or infinite distance from the diffracting system.Diffraction is chiefly of two types - Fraunhofer Diffraction and Fresnel Diffraction.Diffraction occurs with all waves which include water waves, sound waves, electromagnetic waves.The phenomena of diffraction can be observed if the size of the opening is relative to the size of the wavelength of light.Diffraction of light is defined as the slight bending of light waves around the border of a slit or an object.Diffraction object gives rise to wavefronts that are also straight or plane.ĭifference between Diffraction and InterferenceĬoherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves.To produce a diffraction pattern, the plane or horizontal wavefront is connected by means of a convex lens.The incident wavefronts on the diffracting obstacle are horizontal or plane.The screen and the source are infinite from each other.
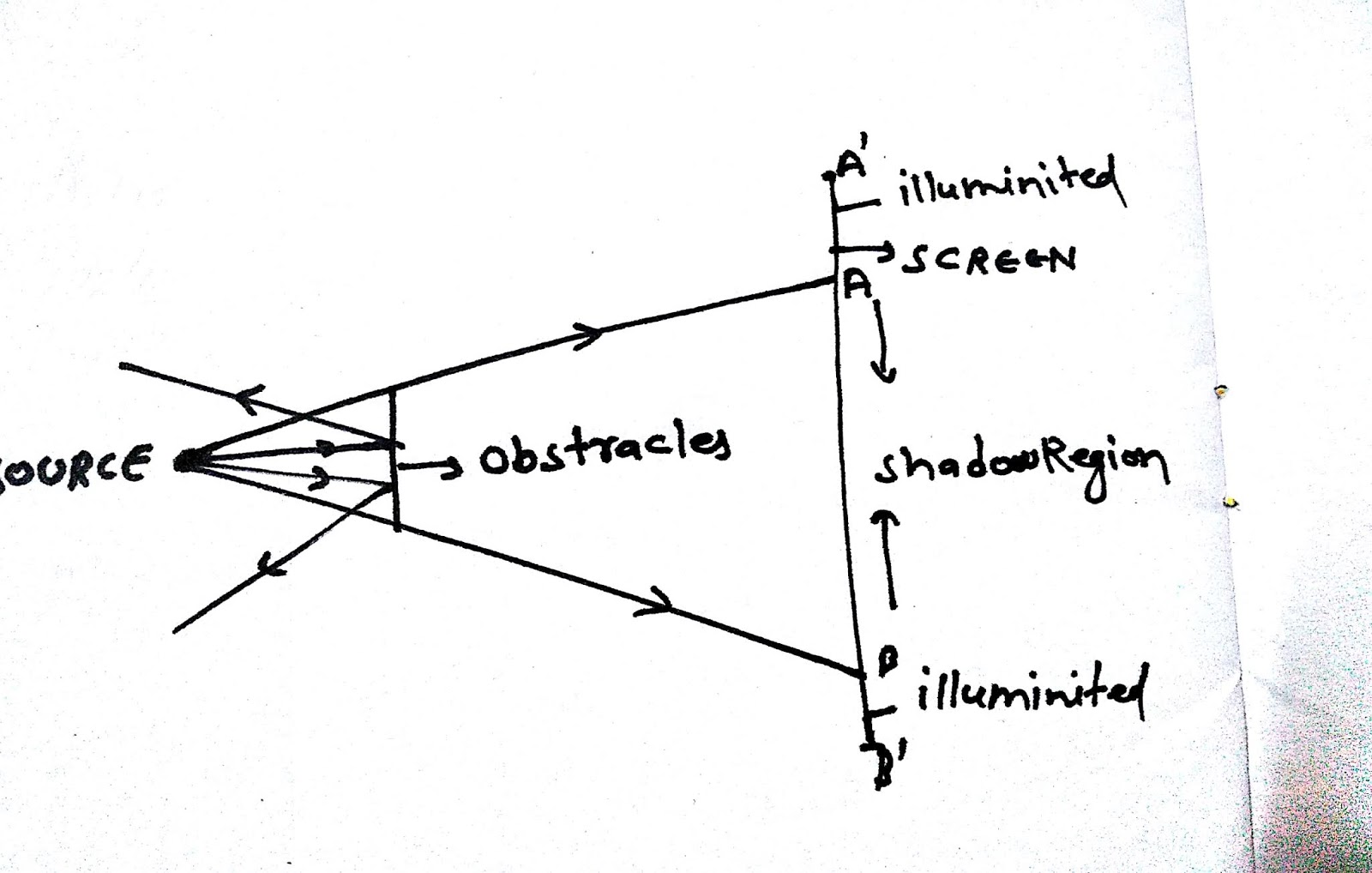
The important points for Fraunhofer Diffraction are discussed in the below points: Fraunhofer Diffraction occurs when the distance is increased and the outgoing diffracted wave becomes straight or horizontal. By using a convex lens, the diffraction pattern is obtained. Resolving Power of Microscopes and Telescopesĭiffraction is primarily categorized into two types -įraunhofer Diffraction is defined as the source of light and the screen in which the pattern of diffraction is obtained effectively at the limitless or infinite distance from the diffracting system. Transmission, Absorption and Reflection of Light The proposed dictionary matching approach permits segmentation, anomaly detection, and indexing to be performed in a unified manner with the additional benefit of uncertainty quantification.ĮBSD Von Mises–Fisher mixture distribution dictionary matching dynamical electron scattering electron backscatter diffraction pattern maximum likelihood orientation estimates.Interference of Light Waves and Young’s Experiment The mean orientation is estimated using a maximum likelihood approach that models the orientation distribution as a mixture of Von Mises-Fisher distributions over the quaternionic three sphere. Indexing is accomplished by computing the mean orientation of the closest matches to each pattern. It classifies a pixel as being near a grain boundary if the highly ranked patterns in the dictionary differ significantly over the pixel's neighborhood.
The DT classifies a pattern as an anomaly if it has an abnormally low similarity to any pattern in the dictionary. The statistical distribution of these closest matches is used in an unsupervised binary decision tree (DT) classifier to identify grain boundaries and anomalous regions. For each measured pattern, we identify the most similar patterns in the dictionary, and identify boundaries, detect anomalies, and index crystal orientations. We discretize the domain of a dynamical forward model onto a dense grid of orientations, producing a dictionary of patterns. We propose a framework for indexing of grain and subgrain structures in electron backscatter diffraction patterns of polycrystalline materials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
